Sax PE. Lancet 2015; 385:2606-15 ; Wohl D. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2016; 72:58-64 ; Arribas JR. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2017 ;75:211-18
Type of ARV Trial
Head-to-head comparative trials for first line ART since 2006
» NRTI combinations
» FTC/TDF vs FTC/TAF or E/C/F/TDF vs E/C/F/TAF
Head-to-head comparative trials for first line ART since 2006
» NRTI combinations
» FTC/TDF vs FTC/TAF or E/C/F/TDF vs E/C/F/TAF
Drugs
E/C/F/TAF, E/C/F/TDF, FTC/TAF, FTC/TDF, TAF, TDF, FTC
E/C/F/TAF, E/C/F/TDF, FTC/TAF, FTC/TDF, TAF, TDF, FTC
- Summary of week 48 results
- E/C/F/TAF QD is virologically non inferior to E/C/F/TDF QD
- 92% of patients treated with E/C/F/TAF achieved virologic suppression through week 48
- High and similar response rates, irrespective of baseline HIV RNA and CD4 cell count, age, sex, race
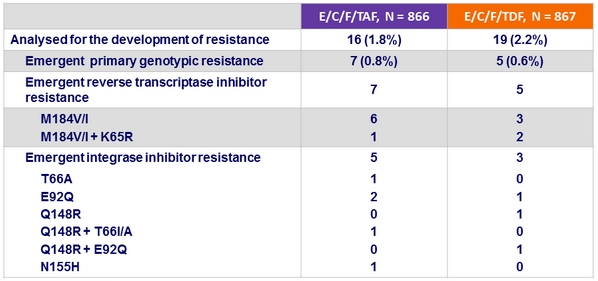
- Low rates of virologic failure, with resistance emergence < 1% in both arms
- CD4 response from baseline significantly higher with E/C/F/TAF
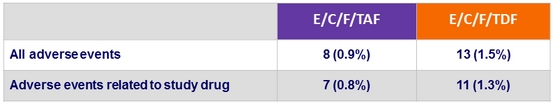
- Discontinuation because of adverse events: 0.9 % vs 1.5 %
- Discontinuation due to renal events: 0 vs 4
- Common adverse events occurred at similar frequency in both arms
- No case of proximal tubulopathy
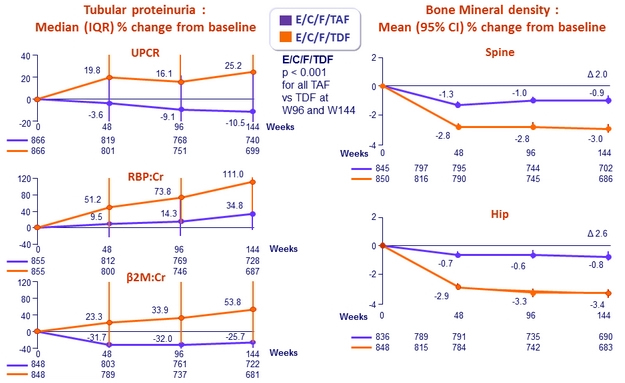
- Compared with E/C/F/TDF, E/C/F/TAF demonstrated
- Significantly smaller decreases in eGFR
- Significantly less proteinuria, albuminuria, and tubular proteinuria
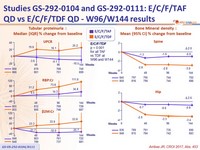
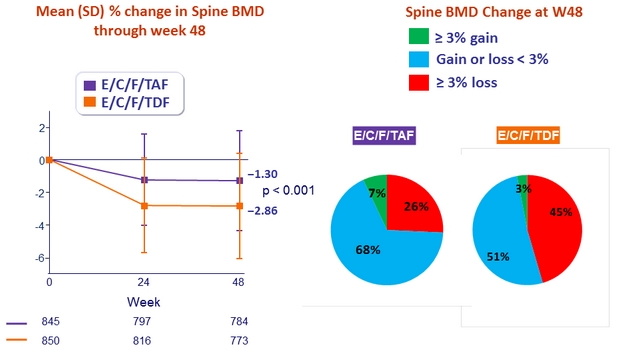
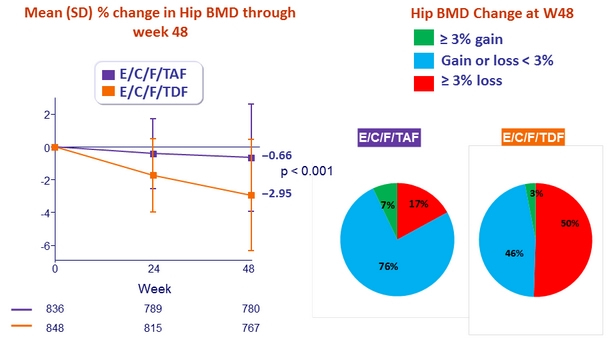
- Significantly less impact on spine and hip BMD
- Greater increases in fasting lipids
Design
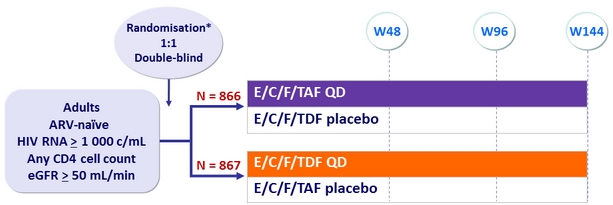
* Randomisation was stratified by HIV RNA (≤ or > 100,000 c/mL), CD4 cell count at screening,
and geographic region
Objective :
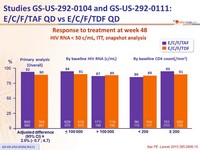
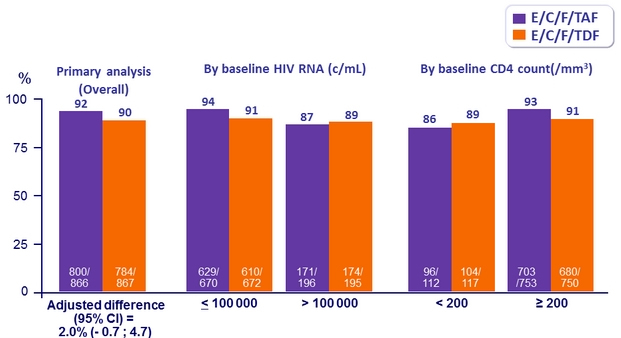
- Non inferiority of E/C/F/TAF at W48: % HIV RNA < 50 c/mL by intention to treat, snapshot analysis (lower margin of the 95% CI for the difference = -12%)
- Safety: serum creatinine , proteinuria, hip BMD, spine BMD
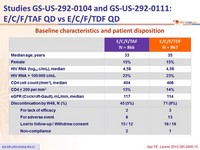
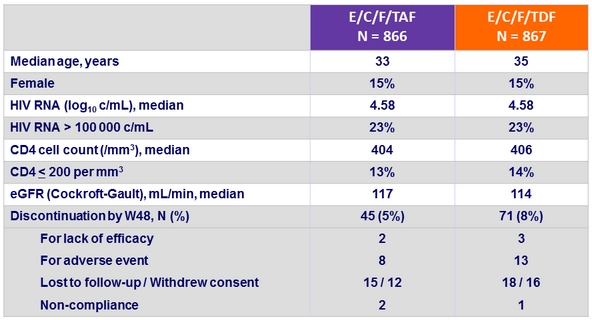
Baseline characteristics and patient disposition
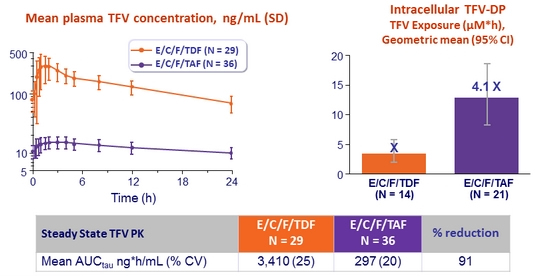
Plasma TFV and intracellular TFV-DP levels
- Intensive PK substudy :
- E/C/F/TAF, N = 36 (PBMC substudy : 21/36)
- E/C/F/TDF, N = 29 ( PBMC substudy : 14/29)
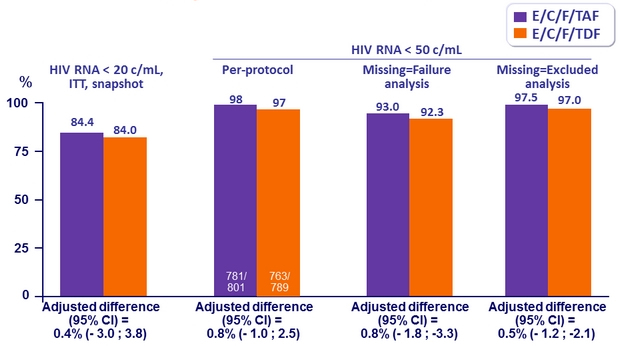
Response to treatment at week 48
HIV RNA < 50 c/mL, ITT, snapshot analysis
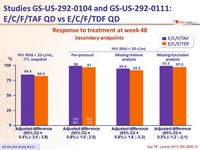
Secondary endpoints
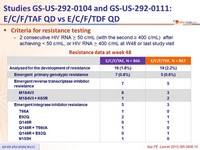
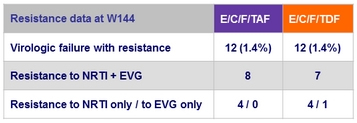
Criteria for resistance testing
- 2 consecutive HIV RNA ≥ 50 c/mL (with the second ≥ 400 c/mL ) after achieving < 50 c/mL , or HIV RNA ≥ 400 c/mL at W48 or last study visit
Resistance data at week 48
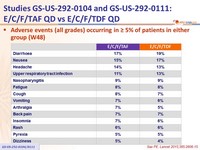
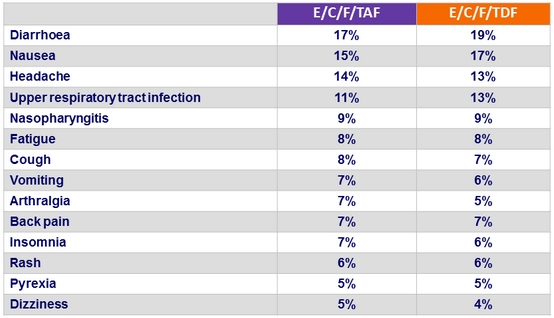
Adverse events (all grades) occurring in ≥ 5% of patients in either group (W48)
Adverse events leading to study drug discontinuation
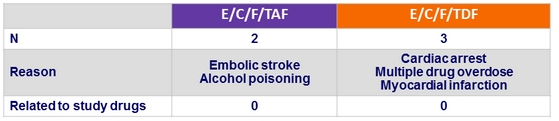
Deaths
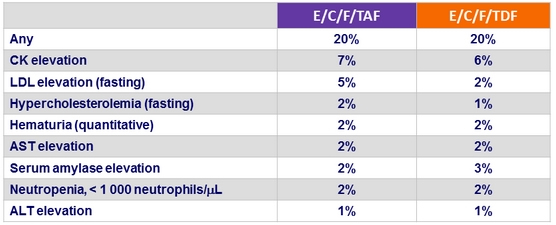
Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities in ≥ 1% of patients in either group (W48)
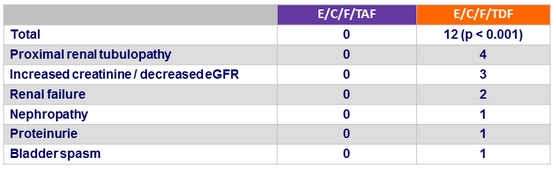
Discontinuation for renal event
- E/C/F/TAF = 0
- E/C/F/TDF = 4 : renal failure = 2, decreased GFR = 1, nephropathy = 1
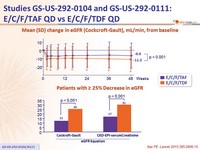
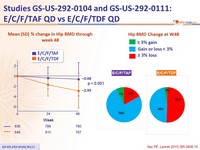
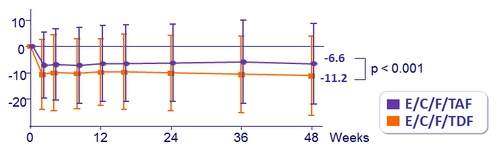
Mean (SD) change in eGFR (Cockcroft-Gault), mL /min, from baseline
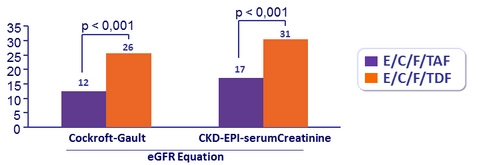
Patients with ≥ 25% Decrease in eGFR
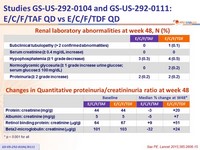
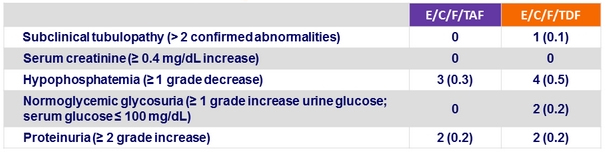
Renal laboratory abnormalities at week 48, n (%)
Changes in Quantitative proteinuria/creatininuria ratio at week 48
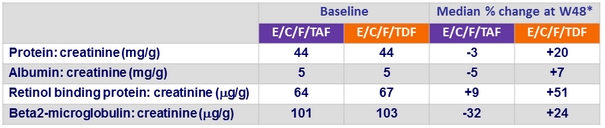
* p < 0.001 for all
Fasting Lipids at Week 48
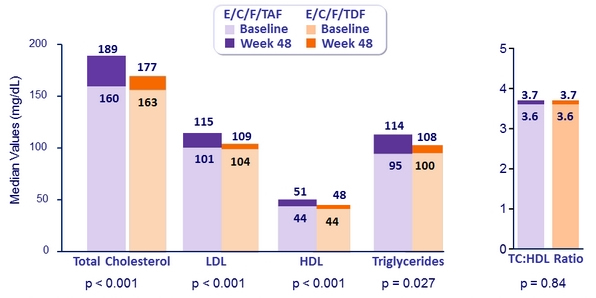
Patients initiating lipid-modifying medications: 3.6% E/C/F/TAF vs 2.9% E/C/F/TDF (p = 0.42)
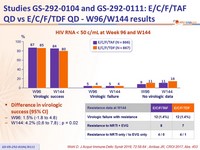
HIV RNA < 50 c/mL at Week 96 and W144
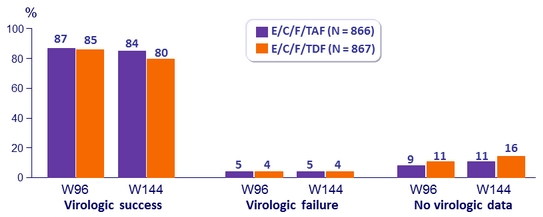
Difference in virologic success (95% CI)
- W96: 1.5% (-1.8 to 4.8)
- W144: 4.2% (0,6 to 7,8) ; p = 0.02
Renal events leading to treatment discontinuation at W144
Adverse events leading to treatment discontinuation at W144
- 1.3% E/C/F/TAF vs 3.3% E/C/F/TDF (p = 0.01)
Grade 3-4 adverse events
- No difference between both groups at W144, except for
- LDL-cholesterol increase: 11.0% E/C/F/TAF vs 4.8% E/C/F/TDF
- Total cholesterol increase: 4.7% vs 2.8%
- Lipase increase: 5.0% vs 8.0%
- Amylase increase: 2.6% vs 5.0%