Gatell JM. Clin Infect Dis. 2007 Jun 1;44(11):1484-92
Type of ARV Trial
Switch studies in virologically suppressed patients
» Switch to ATV or ATV-r
» ATV + 2 NRTI or ATV/r + 2 NRTI vs LPV/r + 2 NRTI
Switch studies in virologically suppressed patients
» Switch to ATV or ATV-r
» ATV + 2 NRTI or ATV/r + 2 NRTI vs LPV/r + 2 NRTI
Drugs
ATV/r, ATV, LPV/r, 2 NRTI
ATV/r, ATV, LPV/r, 2 NRTI
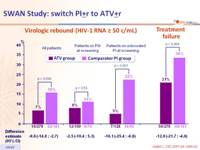
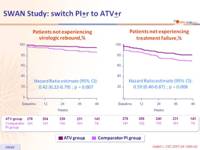
- Switching to a simplified PI-based regimen containing ATV provided better maintenance of virologic suppression with lower rates of virologic rebound and treatment failure than those observed with continued, unmodified therapy
- Safety and tolerability were similar in both groups
- But lipid parameters improved in the ATV group
- Hyperbilirubinemia was frequent on ATV
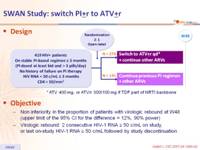
Design :
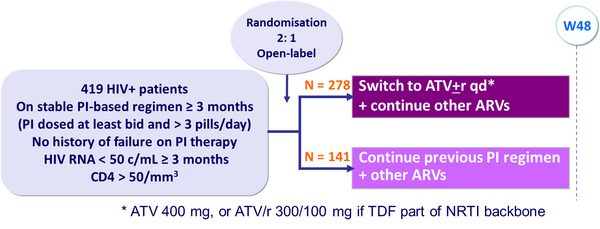
Objective :
- Non inferiority in the proportion of patients with virologic rebound at W48 (upper limit of the 95% CI for the difference = 12%, 90% power)
- Virologic rebound: 2 consecutive HIV-1 RNA ≥ 50 c/mL on study, or last on-study HIV-1 RNA ≥ 50 c/mL followed by study discontinuation
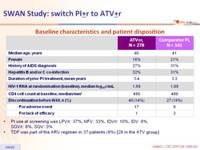
Baseline characteristics and patient disposition :
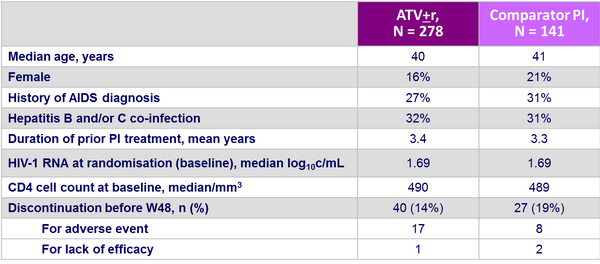
- PI use at screening was LPV/r: 37%, NFV: 33%, IDV/r: 10%, IDV: 8%, SQV/r: 6%, SQV: 3%
- TDF was part of the ARV regimen in 37 patients (9%) [26 in the ATV group]
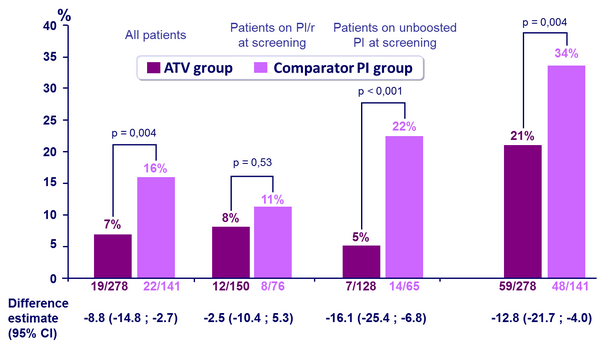
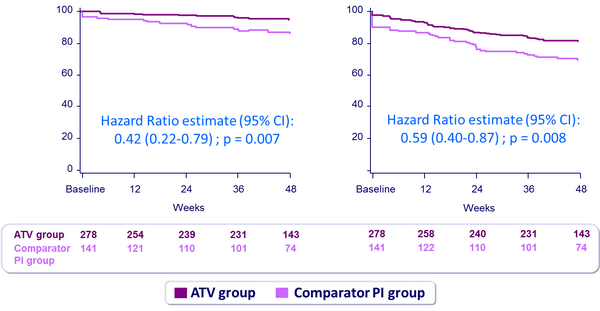
Virologic rebound (HIV-1 RNA ≥ 50 c/mL)
Treatment failure
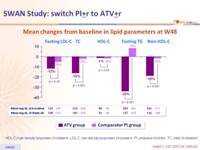
Fasting plasma lipids changes from baseline to week 48 :
Mean changes from baseline in lipid parameters at W48 :
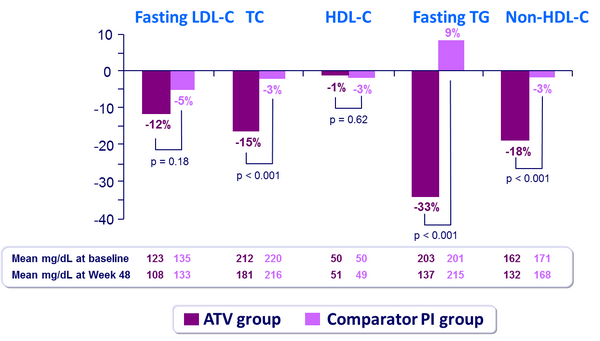
HDL-C,high density lipoprotein cholesterol ; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol ; PI, protease inhibitor ; TC, total cholesterol
Adverse events by W48 :
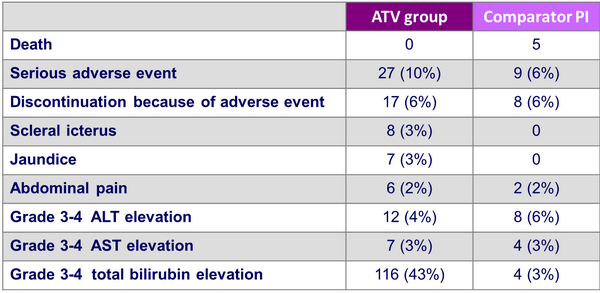
AST and ALT elevations were more frequent in patients with hepatitis co-infection