Margolis DA. Lancet. 2017 Sep 23;390(10101):1499-1510.
Switch studies in virologically suppressed patients
» Switch to INSTI + NNRTI
» CAB LA + RPV LA IM
CAB LA, RPV LA, ABC/3TC
- LATTE-2 results successfully demonstrate ability to maintain HIV-1 RNA < 50 c/mL with IM CAB + RPV LA, dosed every 4 or 8 weeks
- Three subjects met PDVF criteria during maintenance
- Q8W (N = 2), oral CAB (N = 1) ; one Q8W subject with emergent RPV and CAB resistance, and one Q8W subject with minor INSTI mutation emergence
- Injection tolerability
- Majority of ISRs were grade 1 to 2 pain, with a median duration of 3 days
- Few subjects had an ISR that led to discontinuation, with higher rate in Q4W group
- High overall reported satisfaction
- Dose selection
- Q4W dosing resulted in lower rates of virologic non-response with similar safety to Q8W
- Q4W dosing was selected for pivotal phase III studies
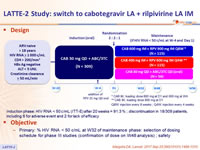
Design

* CAB IM, loading dose 800 mg at D1 and 600 mg at W4
** CAB IM, loading dose 800 mg at D1
Q8W: injection every 8 weeks ; Q4W: injection every 4 weeks
Objective
- Primary: % HIV RNA < 50 c/mL at W32 of maintenance phase: selection of dosing schedule for phase III studies (confirmation of dose on W48 analysis) ; safety
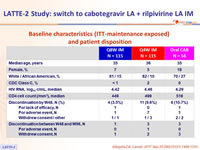
Baseline characteristics (ITT-maintenance exposed) and patient disposition

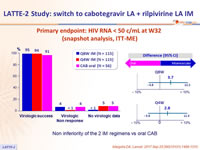
Primary endpoint: HIV RNA < 50 c/mL at W32 (snapshot analysis, ITT-ME)

Non inferiority of the 2 IM regimens vs oral CAB
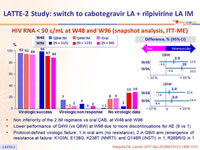
HIV RNA < 50 c/mL at W48 and W96 (snapshot analysis, ITT-ME)

- Non inferiority of the 2 IM regimens vs oral CAB, at W48 and W96
- Lower performance of Q4W (vs Q8W) at W96 due to more discontinuations for AE (9 vs 1)
- Protocol-defined virologic failure: 1 in oral arm (no resistance) , 2 in Q8W arm (emergence of resistance at failure: K103N, E138G, K238T (NNRTI) and Q148R (INSTI) in 1, R269R/G in 1
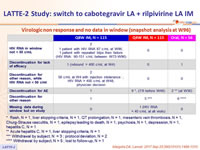
Virologic non response and no data in window (snapshot analysis at W96)

* Rash, N = 1, liver stopping criteria, N = 1, QT prolongation, N = 1, mesenteric vein thrombosis, N = 1, Churg -Strauss vasculitis, N = 1, epilepsy leading to death, N = 1, psychosis, N = 1, depression, N = 1, hepatitis C, N = 1
** Acute hepatitis C, N = 1, liver stopping criteria, N = 1
*** Withdrawal by subject, N = 3 ; protocol deviation, N = 2
**** Withdrawal by subject , N = 5 ; lost to follow-up, N = 1
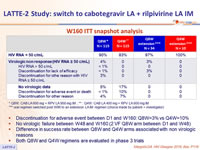
W160 ITT snapshot analysis

* Q8W: CAB LA 600 mg + RPV LA 900 mg IM ; ** : Q4W: CAB LA 400 mg + RPV LA 600 mg IM
*** oral regimen switched post W96 to an extension LA IM regimen (choice made by patient + investigator)
- Discontinuation for adverse event between D1 and W160: Q8W=3% vs Q4W=10%
- No virologic failure between W48 and W160 (2 VF Q8W arm between D1 and W48)
- Difference in success rate between Q8W and Q4W arms associated with non virologic reasons
- Both Q8W and Q4W regimens are evaluated in phase 3 trials
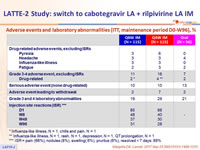
Adverse events and laboratory abnormalities (ITT, maintenance period D0-W96), %

* Influenza-like illness, N = 1, chills and pain, N = 1
** Influenza-like illness, N = 1, rash, N = 1, depression, N = 1, QT prolongation, N = 1
*** ISR = pain (66%), nodules (8%), swelling( 6%), pruritus (6%), resolved < 7 days: 89%
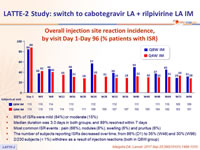
Overall injection site reaction incidence, by visit Day 1-Day 96 (% patients with ISR)

- 99% of ISRs were mild (84%) or moderate (15%)
- Median duration was 3.0 days in both groups, and 89% resolved within 7 days
- Most common ISR events : pain (66%), nodules (8%), swelling (6%) and pruritus (6%)
- The number of subjects reporting ISRs decreased over time, from 86% (D1) to 35% (W48) and 30% (W96)
- 2/230 subjects (< 1%) withdrew as a result of injection reactions (both in Q8W group)
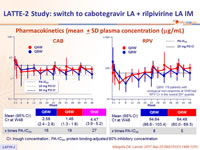
Pharmacokinetics (mean ± SD plasma concentration (mg/mL)

CÏ„, trough concentration ; PA-IC90, protein binding-adjusted 90% inhibitory concentration
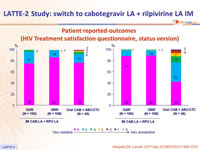
Patient reported-outcomes (HIV Treatment satisfaction questionnaire, status version)