Ofotokun J. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2012 Oct;28(10):1196-206
Type of ARV Trial
Switch studies in virologically suppressed patients
» Switch to RAL + PI/r
» RAL + LPV/r
Switch studies in virologically suppressed patients
» Switch to RAL + PI/r
» RAL + LPV/r
Drugs
RAL, LPV/r
RAL, LPV/r
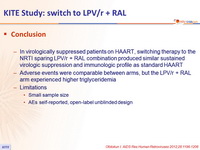
- In virologically suppressed patients on HAART, switching therapy to the NRTI sparing LPV/r + RAL combination produced similar sustained virologic suppression and immunologic profile as standard HAART
- Adverse events were comparable between arms, but the LPV/r + RAL arm experienced higher triglyceridemia
- Limitations
- Small sample size
- AEs self-reported, open-label unblinded design
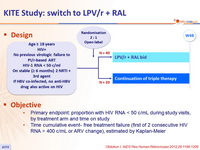
Design
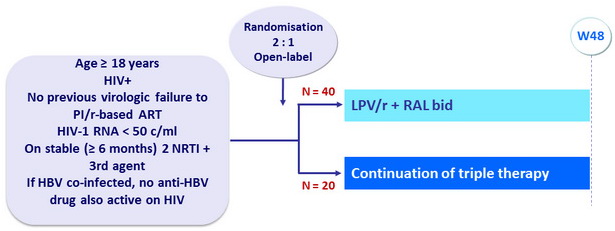
Objective
- Primary endpoint: proportion with HIV RNA < 50 c/mL during study visits, by treatment arm and time on study
- Time cumulative event- free treatment failure (first of 2 consecutive HIV RNA > 400 c/mL or ARV change), estimated by Kaplan-Meier
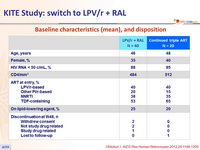
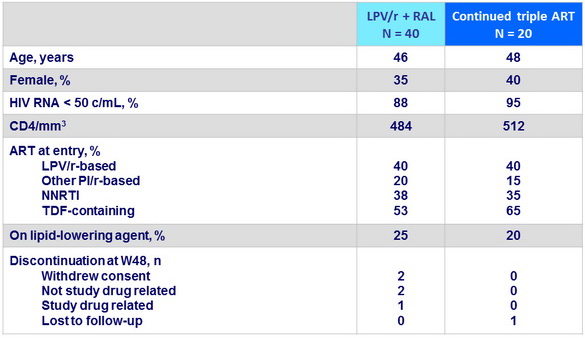
Baseline characteristics (mean), and disposition
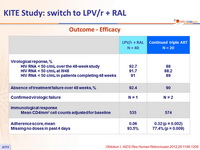
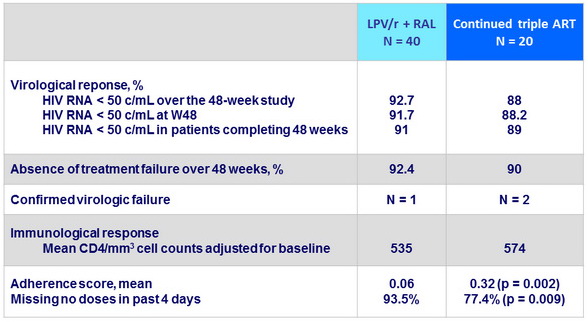
Outcome - Efficacy
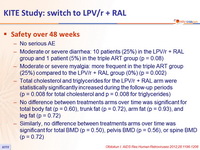
Safety over 48 weeks
- No serious AE
- Moderate or severe diarrhea: 10 patients (25%) in the LPV/r + RAL group and 1 patient (5%) in the triple ART group (p = 0.08)
- Moderate or severe myalgia: more frequent in the triple ART group (25%) compared to the LPV/r + RAL group (0%) (p = 0.002)
- Total cholesterol and triglycerides for the LPV/r + RAL arm were statistically significantly increased during the follow-up periods (p = 0.008 for total cholesterol and p = 0.008 for triglycerides)
- No difference between treatments arms over time was significant for total body fat (p = 0.60), trunk fat (p = 0.72), arm fat (p = 0.93), and leg fat (p = 0.72)
- Similarly, no difference between treatments arms over time was significant for total BMD (p = 0.50), pelvis BMD (p = 0.56), or spine BMD (p = 0.72)