Molina JM, Lancet HIV 2018;5:e211-20 ; Molina JM, IAC 2018, Abs. LBPEB017
Head-to-head comparative trials for first line ART since 2006
» NNRTI vs PI/r
» DOR + 2 NRTI vs DRV/r + 2 NRTI
DRV/r, DOR, 2 NRTI
- Conclusion at week 96
- In HIV-1 infected treatment-naïve participants at W96, DOR in combination therapy with 2 NRTI demonstrated
- Higher efficacy compared to DRV/r
- Low rate of resistance with only 2/383 (0.5%) participants on DOR developing resistance to any study drug through W96
- Doravirine was generally safe and well tolerated
- Low rate of discontinuations due to adverse events
- Favorable lipid profile compared with DRV/r
- In HIV-1 infected treatment-naïve participants at W96, DOR in combination therapy with 2 NRTI demonstrated
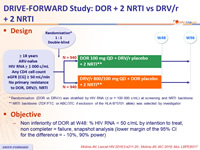
Design :
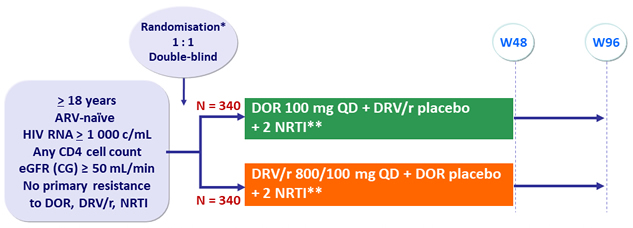
* Randomisation (DOR vs DRV/r) was stratified by HIV RNA ( < or > 100 000 c/mL) at screening and NRTI backbone
** NRTI backbone (TDF/FTC or ABC/3TC if exclusion of the HLA-B*5701 allele) was selected by investigator
Objective :
- Non inferiority of DOR at W48: % HIV RNA < 50 c/mL by intention to treat, non completer = failure, snapshot analysis (lower margin of the 95% CI for the difference = - 10%, 90% power)
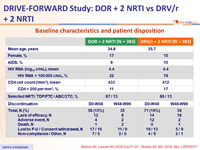
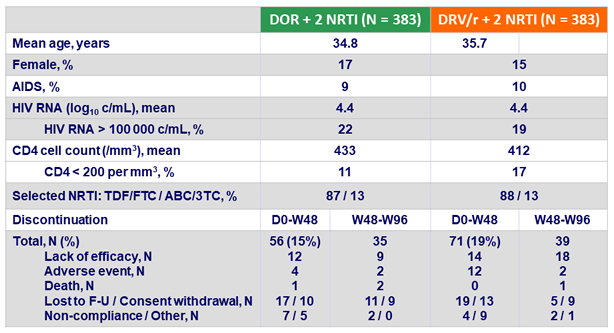
Baseline characteristics and patient disposition
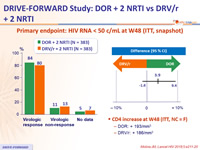
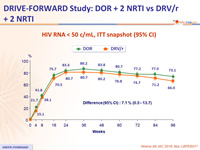
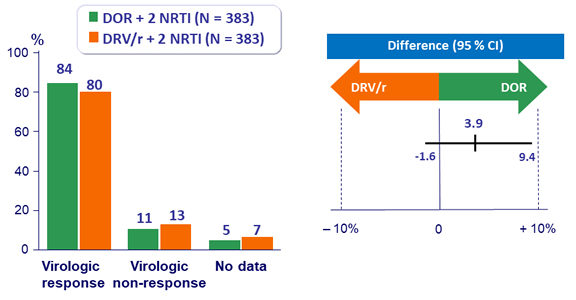
Primary endpoint: HIV RNA < 50 c/mL at W48 (ITT, snapshot)
- CD4 increase at W48 (ITT, NC = F)
- DOR: + 193/mm3
- DRV/r: + 186/mm3
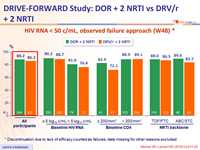
HIV RNA < 50 c/mL, observed failure approach (W48) *
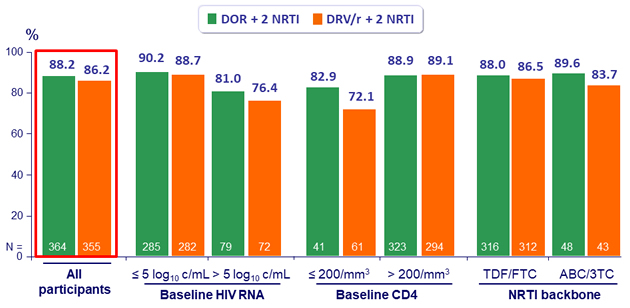
* Discontinuation due to lack of efficacy counted as failures, data missing for other reasons excluded
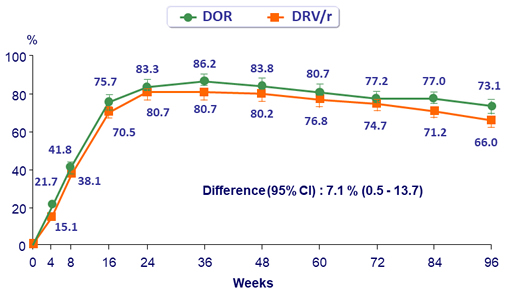
HIV RNA < 50 c/mL, ITT snapshot (95% CI)
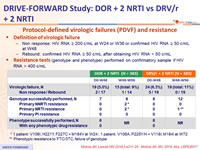
Protocol-defined virologic failures (PDVF) and resistance
- Definition of virologic failure
- Non response: HIV RNA ≥ 200 c/mL at W24 or W36 or confirmed HIV RNA ≥ 50 c/mL at W48
Rebound: confirmed HIV RNA ≥ 50 c/mL after obtaining HIV RNA < 50 c/mL
- Non response: HIV RNA ≥ 200 c/mL at W24 or W36 or confirmed HIV RNA ≥ 50 c/mL at W48
- Resistance tests (genotype and phenotype) performed on confirmatory sample if HIV RNA > 400 c/mL
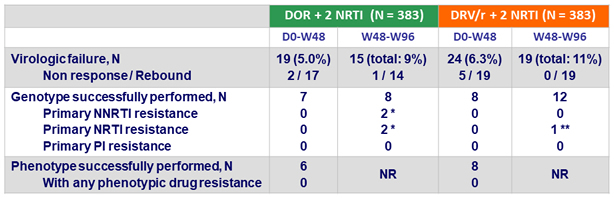
* 1 patient: V106I, H221Y, F227C + M184V at W24 ; 1 patient: V106A, P225Y/H + V118I, M184I at W72
** Phenotypic resistance to FTC/3TC, failure of genotype
Emergence of drug resistance in participants with discontinuations by W48
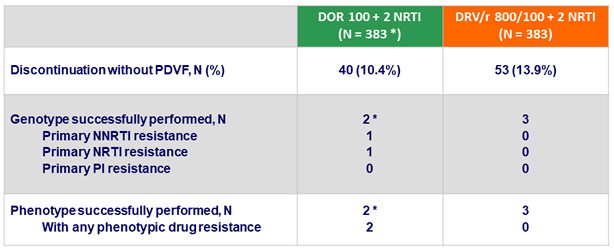
*
1 discontinuation for non-compliance at W24, with emergence of resistance to DOR (V106I + H221Y ; > 90 fold increased IC50) and FTC (M184V) ; 1 discontinuation for rash at W2, with increased DOR IC50 2.8 fold WT (resistance cutoff = 2.5 fold), but no genotypic resistance mutations
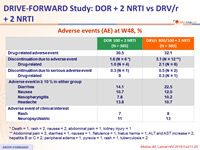
Adverse events (AE) at W48, %
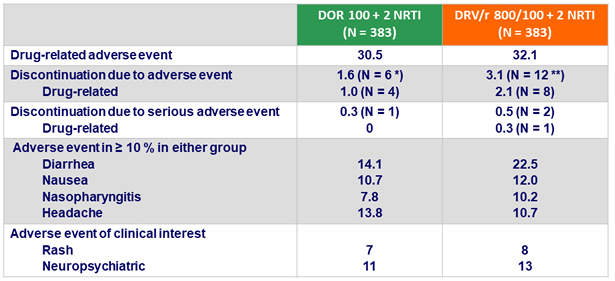
* Death = 1, rash = 2, nausea = 2, abdominal pain = 1, kidney injury = 1
** Abdominal pain = 2, diarrhea = 1, nausea = 1, flatulence = 1, hiatus hernia = 1, ALT and AST increase = 2, hepatitis B or C = 2, peripheral edema = 1, pyrexia = 1, rash = 1, tuberculosis = 2
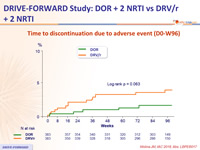
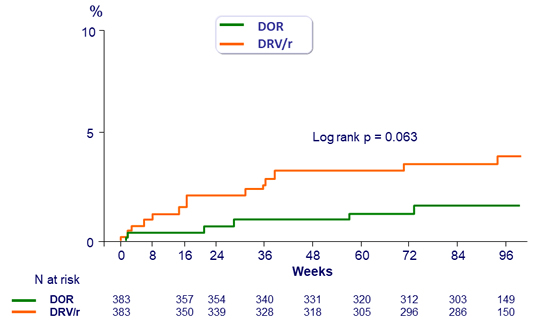
Time to discontinuation due to adverse event (D0-W96)
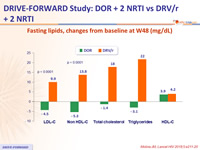
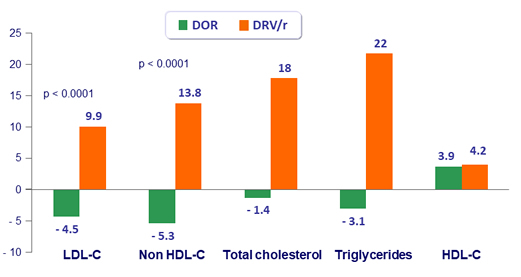
Fasting lipids, changes from baseline at W48 (mg/dL)
Conclusion at Week 48
- DOR 100 mg QD, in combination with either TDF/FTC or ABC/3TC
- Achieved high virologic success at week 48
- And was non-inferior to DRV/r + 2 NRTI regardless of baseline HIV RNA
- Resistance mutations through 48 weeks
- None were detected in protocol-defined virologic failures
- Only 1/383 participants on DOR developed genotypic and phenotypic resistance to DOR + FTC/3TC
- Adverse events leading to discontinuation occurred with low frequency for both DOR and DRV/r
- Low rate of discontinuation due to rash or neuropsychiatric adverse events
- Lipid changes were less pronounced for DOR than for DRV/r
- Once-daily DOR in combination with fixed-dose NRTIs represents an effective treatment option for HIV-1-infected, treatment-naive patients