Wijting I. Lancet HIV 2017; 4:e547-54; J Infect Dis. 2018 ;218:688-97
Type of ARV Trial
Switch studies in virologically suppressed patients
» Switch to DTG-containing regimen
» DTG monotherapy
Switch studies in virologically suppressed patients
» Switch to DTG-containing regimen
» DTG monotherapy
Drugs
DTG
DTG
- DTG monotherapy, as switch strategy in virologically suppressed patients, is
- Suboptimal
- Associated with virologic failure in a relatively high number of patients
- And emergence of INSTI resistance
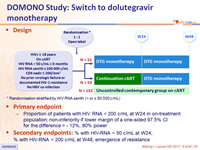
Design
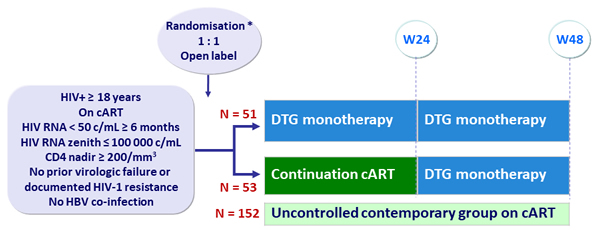
* Randomisation stratified by HIV RNA zenith (< or > 50 000 c/mL)
Primary endpoint
- Proportion of patients with HIV RNA < 200 c/mL at W24 in on-treatment population; non-inferiority if lower margin of a one-sided 97.5% CI for the difference = - 12%, 80% power
Secondary endpoints
- % with HIV-RNA < 50 c/mL at W24, % with HIV-RNA < 200 c/mL at W48, emergence of resistance
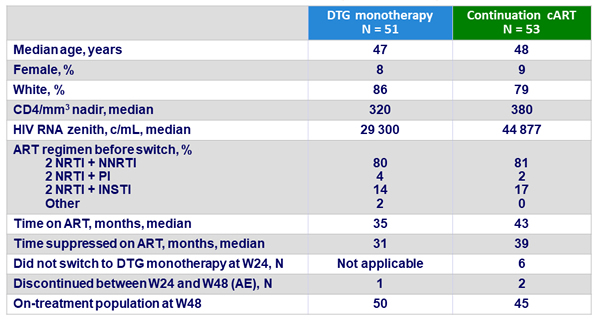
Baseline characteristics and patient disposition
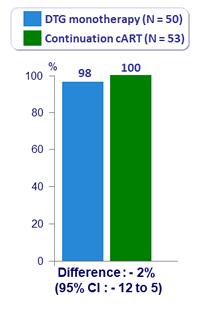
HIV RNA < 200 c/mL at W24
- HIV RNA < 200 c/mL at W48
- DTG monotherapy (immediate and deferred switch group) = 87/95 (92%)
- Concurrent uncontrolled group on cART = 149/152 (98%)
- Difference = - 6% (95% CI: - 14.5 to - 0.5)
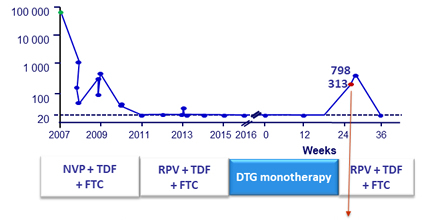
- Follow-up on DTG monotherapy (immediate and deferred switch group)
- 8 virologic failures (2 before W24, 6 after W24)
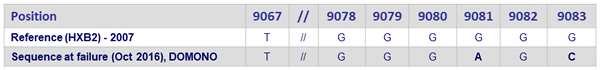
- Integrase genotype at failure successful in 6/8: emergence of resistance mutations in 3/6 [N155H ; S230R ; R263K]
- In all patients with virologic failure, DTG plasma concentrations were therapeutic and self-reported adherence was > 95%
- 1 patient with no new resistance mutations in integrase gene at virologic failure, but with mutations in nef/LTR region (Sanger sequencing)
HIV RNA (c/mL)
Changes in the G-stretch of the 3’-PPT (nef)