Malan DR. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2008 Feb 1;47(2):161-7
Type of ARV Trial
Head-to-head comparative trials for first line ART since 2006
» PI vs PI
» ATV + 3TC + d4T vs ATV/r + 3TC + d4T
Head-to-head comparative trials for first line ART since 2006
» PI vs PI
» ATV + 3TC + d4T vs ATV/r + 3TC + d4T
Drugs
ATV/r, ATV, 3TC, d4T
ATV/r, ATV, 3TC, d4T
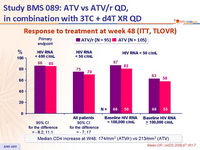
- For first-line antiretroviral therapy, ATV/r 300/100 mg QD was virologically non inferior to ATV 400 mg QD, when combined with 3TC and d4T XR QD
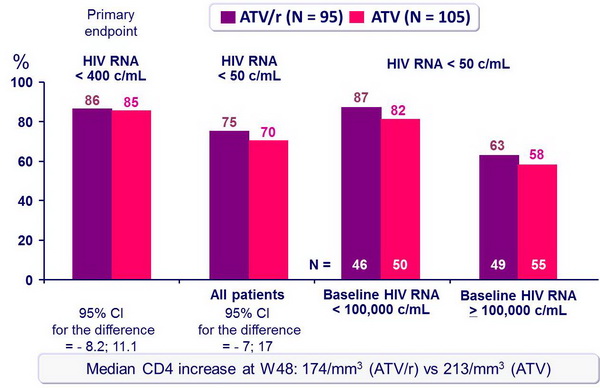
- Response rate at an HIV RNA < 50 c/mL at W48 was 25% less in patients with baseline HIV RNA > 100,000 c/mL as compared with baseline HIV RNA < 100,000 c/mL
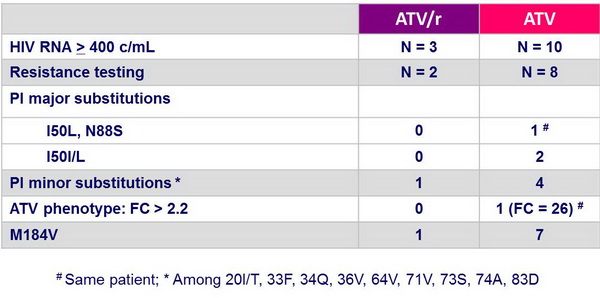
- Virologic failure occurred more frequently in the ATV group (9.5% vs 3.2%) with emergence of major atazanavir-associated mutations in 3/8 tested patients in the ATV group
- Results (HIV RNA < 50 c/mL at W48, virologic failure rate, resistance data) suggest ATV/r is more potent than ATV
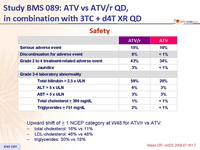
- Discontinuation due to treatment-related adverse event occurred more frequently in the ATV/r group
- Increases in total cholesterol and triglycerides were greater in the ATV/r group
- Possible impact of stavudine on lipid increases
- Limitation: small size of the study
Design :
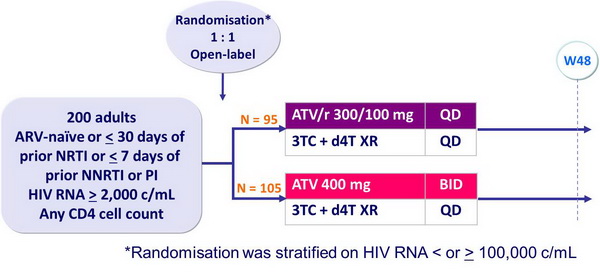
Objective :
- Non inferiority of ATV/r 300/100 vs ATV 400 at W48: % HIV RNA < 400 c/mL, ITT, TLOVR algorithm (lower margin of the 95% CI for the difference = -10%, 80% power)
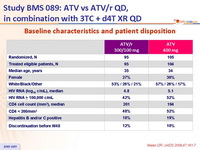
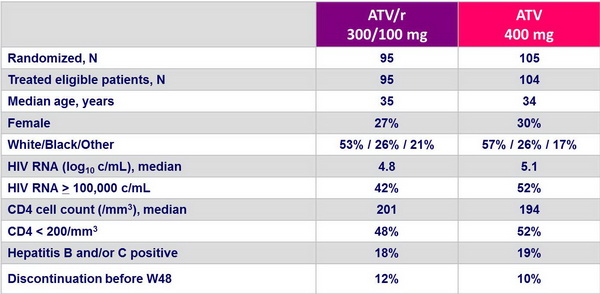
Baseline characteristics and patient disposition :
Response to treatment at week 48 (ITT, TLOVR) :
Treatment-emergent resistance :
Safety :
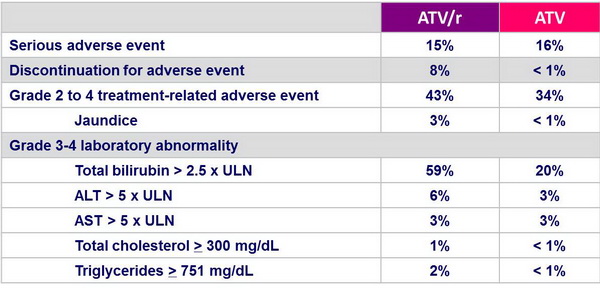
- Upward shift of > 1 NCEP category at W48 for ATV/r vs ATV:
- total cholesterol: 16% vs 11%
- LDL-cholesterol: 46% vs 48%
- triglycerides: 30% vs 18%