Mallolas J. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2009 May 1;51(1):29-36
Type of ARV Trial
Switch studies in virologically suppressed patients
» Switch to ATV or ATV-r
» ATV/r + 2 NRTI vs LPV/r + 2 NRTI
Switch studies in virologically suppressed patients
» Switch to ATV or ATV-r
» ATV/r + 2 NRTI vs LPV/r + 2 NRTI
Drugs
ATV/r, LPV/r, 2 NRTI
ATV/r, LPV/r, 2 NRTI
- Switching to a simplified PI-based regimen containing ATV/r provides virological suppression and treatment failure similar to those observed with continued unmodified therapy with LPV/r
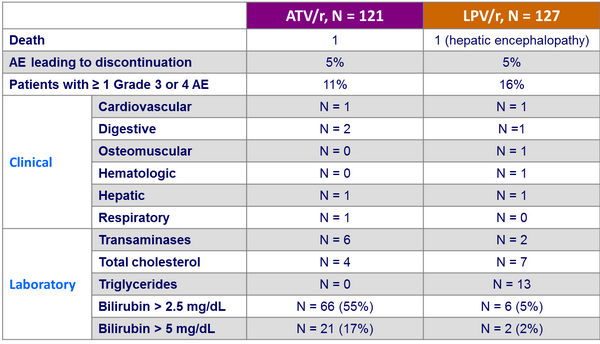
- Safety and tolerability profile were similar in both groups
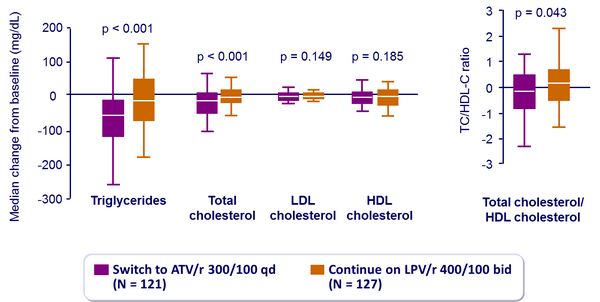
- Improved lipid parameters were observed in the ATV/r arm
- High incidence of hyperbilirubinemia occurred in the ATV/r arm
- Switching patients with virologic suppression on LPV/r to once-daily ATV/r can provide an effective and well-tolerated treatment option
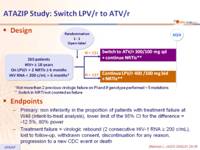
Design :
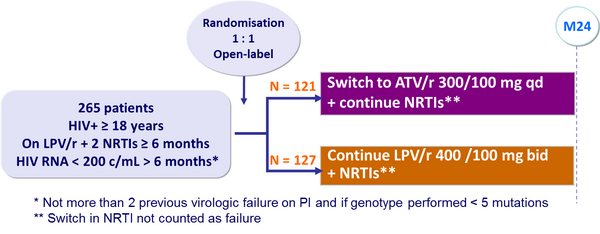
Endpoints :
- Primary: non inferiority in the proportion of patients with treatment failure at W48 (intent-to-treat analysis), lower limit of the 95% CI for the difference = -12.5%, 80% power
- Treatment failure = virologic rebound (2 consecutive HIV-1 RNA ≥ 200 c/mL), lost to follow-up, withdrawn consent, discontinuation for any reason, progression to a new CDC event or death
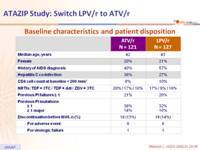
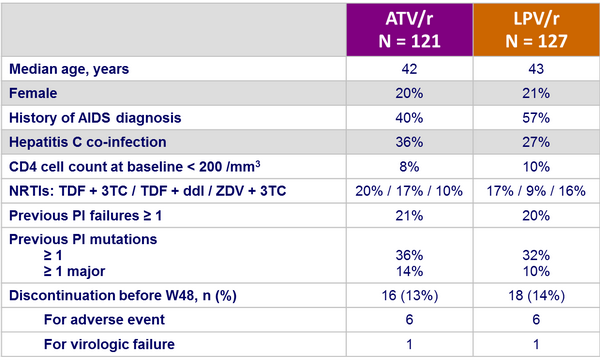
Baseline characteristics and patient disposition :
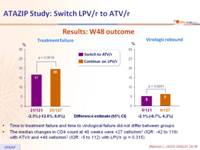
Results: W48 outcome :
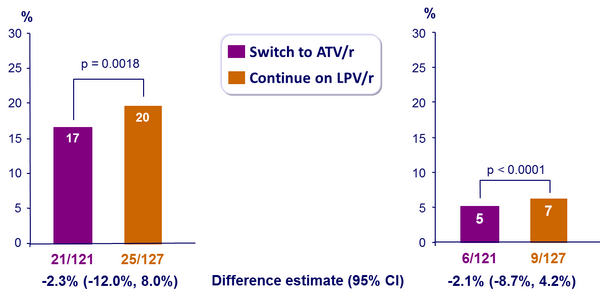
- Time to treatment failure and time to virological failure did not differ between groups
- The median changes in CD4 count at 48 weeks were +27 cells/mm3 (IQR: -42 to 119) with ATV/r and +48 cells/mm3 (IQR: -5 to 112) with LPV/r (p = 0.315)
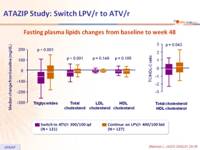
Fasting plasma lipids changes from baseline to week 48 :
Adverse events by W48 :