Sax PE. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2014 Sep 1;67(1):52-8
Type of ARV Trial
Phase 2 of new ARVs
» TAF (TFV prodrug)
» E/C/F/TAF vs E/C/F/TDF
Phase 2 of new ARVs
» TAF (TFV prodrug)
» E/C/F/TAF vs E/C/F/TDF
Drugs
E/C/F/TAF, E/C/F/TDF, EVG/c, FTC/TAF, FTC/TDF, TAF, TDF, FTC
E/C/F/TAF, E/C/F/TDF, EVG/c, FTC/TAF, FTC/TDF, TAF, TDF, FTC
- In this phase 2, randomised clinical trial, HIV-positive treatment-naive adults received STRs of E/c/F/TAF or E/c/F/TDF. Both STRs demonstrated high and comparable rates of virologic suppression through 48 weeks of therapy
- Both regimens were well tolerated, with few discontinuations due to adverse events. Nausea occurred more frequently with E/c/F/TAF
- Plasma concentrations of TFV were substantially (91%) lower with E/c/F/TAF than with E/c/ F/TDF, and the TAF regimen delivered 5.3 times the intracellular, physiologically active metabolite, TFV-DP, to PBMCs, which could translate into less end-organ toxicity and/or improved virologic control
- Significant smaller decreases in bone mineral density through 48 with E/c/F/TAF than with E/c/F/TDF
- Urinary RBP/creatinine and b-2 microglobulin/creatinine ratios were significantly lower in the E/c/F/TAF arm, which suggests that TAF has a lesser effect than TDF on the proximal renal tubular cell
Design :
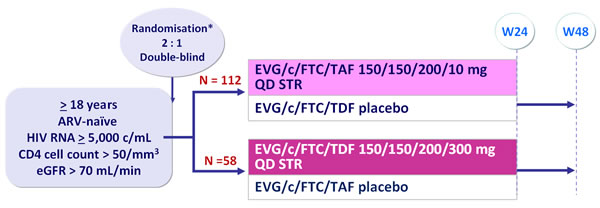
*Randomisation was stratified by HIV RNA (< or > 100,000 c/mL) at screening
Primary objective :
- Determine virologic efficacy of EVG/c/FTC/TAF
- 150 patients provide 76% power to detect a 1.5% (SD of 3.3%) difference in hip bone mineral density in the EVG/c/FTC/TAF arm relative to the EVG/c/FTC/TDF arm
Baseline characteristics of the patients with screening HIV RNA > 100,000 c/mL :
Median viral load at baseline : 4.6 log10 c/mL (21% > 100,000 c/mL), median CD4+ cell count : 391 cells/mm3 (15% > 200/mm3)
Main results :
- Discontinuation due to adverse events by W48 : 4 in TAF arm vs 0 in TDF arm
- HIV RNA < 50 c/mL at W24 : 87.5% E/c/F/TAF vs 89.7% E/c/F/TDF
- 3 patients in each arm met criteria for resistance testing (virologic failure [2 consecutive HIV RNA > 50 c/mL] with HIV RNA > 400 c/mL). Genotype was performed on confirmatory sample
- E/c/F/TAF : no resistance detected
- E/c/F/TDF : 2 patients developed resistance, 1 to NRTI, 1 to INSTI + NRTI
- PK substudy : plasma TFV exposure was 91% lower with E/c/F/TAF than with E/c/F/TDF, as measured by AUCtau. Conversely, intracellular TFV-DP levels in PBMCs were 5.3-fold higher with E/c/F/TAF
Safety :
- Significantly less change in the E/c/F/TAF arm in BMD at hip (-0.62% vs -2.39%, p < 0.001) and lumbar spine (-1.0% vs -3.37%, p < 0.001) at W48, which were also significant at week 24
- In the E/c/F/TAF arm, 32% of patients had no decrease in hip BMD vs 7% in the E/c/F/TDF arm (p < 0.001)
- Median change in eGFR by Cockcroft–Gault = -5.5 mL/min for E/c/F/TAF vs -10.1 mL/min for E/c/F/TDF (p = 0.041)
- Renal tubular proteinuria [urine retinol-binding protein/creatinine ratio and urine b-2 microglobulin/creatinine ratio] was significantly lower in patients who received E/c/F/TAF : no cases of proximal tubulopathy
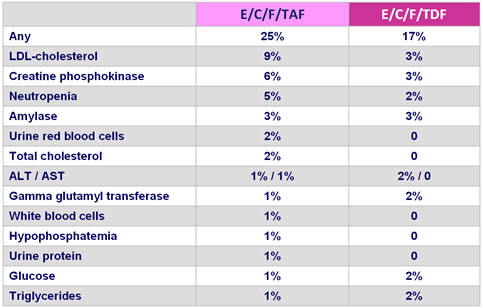
- Grade 3-4 adverse events : 9.8% TAF vs 5.2% TDF
- Most common treatment-emergent adverse events : nausea (21% vs 12%), diarrhea (16% in each arm)
- Higher elevations in lipids with TAF
Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities :